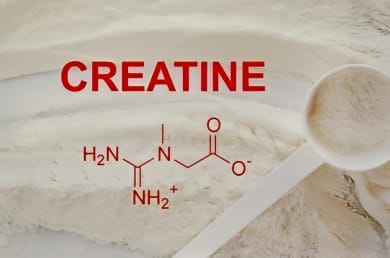
 Creatine is a safe, effective, and affordable supplement that enhances strength, power, muscle growth, and recovery, making it a must-have for athletes and fitness enthusiasts of all levels.
Creatine is a safe, effective, and affordable supplement that enhances strength, power, muscle growth, and recovery, making it a must-have for athletes and fitness enthusiasts of all levels.Creatine is one of the most researched and effective supplements available for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Known for its ability to enhance strength, muscle growth, and endurance, creatine has become a staple in the routines of bodybuilders, powerlifters, and anyone looking to improve their physical performance. In this detailed guide, we will explore the science behind creatine, its numerous benefits, how to use it effectively, and why it is considered one of the most essential supplements in the fitness world.
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in your body’s muscles, primarily stored as phosphocreatine, which is used to produce energy during high-intensity activities. About 95% of your body’s creatine is stored in muscles, while the remaining 5% is found in your brain, kidneys, and liver.
While creatine is naturally present in foods like red meatand fish, the amount you get from these sources is relatively low. This is where creatine supplements come in, allowing you to maximize your muscle stores and optimize your performance.
How Does Creatine Work?
Creatine works by increasing the availability of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary energy currency of your cells. During short bursts of high-intensity activities, such as lifting weights or sprinting, your muscles use ATP for energy. Once ATP is depleted, your performance starts to decline.
Supplementing with creatine increases your stores of phosphocreatine, which helps regenerate ATP more quickly, allowing you to maintain high-intensity efforts for longer periods. This leads to greater power output, strength, and endurance.
The Benefits of Creatine
Creatine has a wide range of benefits, both for athletic performance and overall health. Let’s dive into the top reasons why creatine should be part of your supplement routine:
1. Increases Strength and Power
Creatine is best known for its ability to improve strength and power output during high-intensity activities. Research consistently shows that supplementing with creatine can lead to significant improvements in muscle strength and explosive power. This makes creatine an ideal supplement for athletes involved in strength sports like weightlifting, powerlifting, and bodybuilding.
2. Enhances Muscle Growth
Creatine promotes muscle hypertrophy by increasing the water content in your muscle cells, leading to a fuller, more volumized appearance. Over time, this cellular swelling can trigger processes that lead to increased muscle mass. Additionally, creatine enables you to lift heavier weights and perform more reps, which contributes to long-term muscle growth.
3. Improves High-Intensity Exercise Performance
Whether you’re sprinting, lifting weights, or doing high-intensity interval training (HIIT), creatine can help you perform better. By regenerating ATP more efficiently, creatine allows you to sustain high-intensity efforts for longer, resulting in more productive workouts and better overall performance.
4. Speeds Up Recovery
While creatine is primarily known for its performance-enhancing effects, it also aids in muscle recovery. By reducing muscle damage and inflammation after intense workouts, creatine helps you recover faster and get back to training sooner. This is especially beneficial for athletes who train frequently or at a high intensity.
5. Enhances Brain Function
Creatine is not just for your muscles—it also benefits your brain. Studies have shown that creatine supplementation can improve cognitive performance, particularly in tasks that require short-term memory and quick thinking. This is because your brain, like your muscles, relies on ATP for energy, and creatine helps ensure that energy demands are met, especially during mentally taxing activities.
6. May Improve Endurance
Although creatine is most effective for short bursts of activity, some studies suggest that it can also enhance endurance performance. By improving your body’s ability to sustain high-intensity efforts, creatine may indirectly contribute to better endurance in activities like running, cycling, or swimming.
7. Supports Bone Health
Emerging research suggests that creatine supplementation may help improve bone density by increasing the production of growth factors related to bone strength. This could be particularly beneficial for older adults or anyone at risk of osteoporosis.
How to Use Creatine
Creatine is easy to incorporate into your daily routine, but to maximize its effectiveness, it’s important to understand how to use it properly.
1. The Loading Phase
Some individuals choose to start creatine supplementation with a loading phase to saturate their muscles with creatine more quickly. During the loading phase, you would take 20 grams of creatine per day (split into 4 doses) for 5-7 days. This rapidly increases your muscle creatine stores and allows you to experience the benefits sooner.
2. Maintenance Phase
After the loading phase, you can move on to the maintenance phase, where you take 3-5 grams of creatine per day to maintain your muscle creatine levels. This phase can be sustained indefinitely, as creatine is safe for long-term use.
3. No Loading Phase Option
If you prefer not to do a loading phase, you can take 3-5 grams of creatine daily from the start. This approach will still lead to an increase in muscle creatine stores, but it will take about 3-4 weeks to reach full saturation.
4. Timing
There’s no strict rule on when to take creatine, but research suggests that taking it post-workout may provide the most benefits, as your muscles are more receptive to nutrient uptake after exercise. However, consistency is key, so taking creatine at any time of the day will still be effective.
Types of Creatine
Creatine supplements come in various forms, with the most common being creatine monohydrate.
Here’s a look at the different types of creatine and their effectiveness:
- Creatine Monohydrate: The most well-researched and widely used form of creatine. It’s highly effective, affordable, and the best option for most people.
- Creatine HCL: A more concentrated form of creatine, requiring smaller doses. It may be easier on the stomach for some individuals.
- Buffered Creatine: This form is said to be more stable and less likely to cause stomach discomfort, but it has not been proven to be more effective than monohydrate.
- Creatine Ethyl Ester: A form of creatine that’s marketed as being better absorbed, but studies suggest it’s less effective than monohydrate.
- Micronized Creatine: This is simply creatine monohydrate that has been processed into smaller particles, making it easier to mix and absorb.
Side Effects of Creatine
Creatine is one of the safest supplements available, with decades of research backing its safety for both short-term and long-term use. However, some individuals may experience minor side effects, such as:
- Water Retention: Creatine causes your muscles to hold more water, leading to temporary weight gain. This is not fat gain, but simply water weight, and is not a cause for concern.
- Digestive Issues: Some people may experience stomach discomfort, bloating, or diarrhea, especially during the loading phase. Reducing the dosage or switching to a different form of creatine (such as HCL) can help alleviate these issues.
- Kidney Concerns: There is no evidence that creatine causes kidney damage in healthy individuals, but those with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult a doctor before supplementing.
Who Should Take Creatine?
Creatine is suitable for a wide range of individuals, including:
- Strength Athletes: Powerlifters, bodybuilders, and anyone looking to increase muscle mass and strength can benefit from creatine.
- Endurance Athletes: Runners, cyclists, and swimmers can use creatine to enhance high-intensity efforts and improve recovery.
- Vegetarians and Vegans: Since creatine is primarily found in animal products, vegetarians and vegans may have lower creatine stores and can benefit greatly from supplementation.
- Older Adults: Creatine has been shown to help maintain muscle mass and strength in older adults, potentially reducing the risk of sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss).
Conclusion
Creatine is a powerhouse supplement that offers a wide range of benefits, from increasing strength and power to enhancing muscle growth and recovery. It’s one of the most well-researched and effective supplements on the market, with a strong safety profile for long-term use.
Whether you’re a strength athlete looking to boost performance, an endurance athlete aiming to improve recovery, or someone just getting started on their fitness journey, creatine can provide the edge you need to reach your goals.
By understanding how to use creatine properly and incorporating it into your routine, you can experience noticeable improvements in both performance and muscle development.