Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD)
Understanding PCOD: Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis

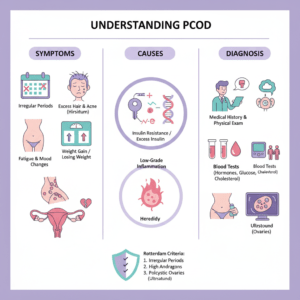
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD), frequently referred to as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), is a common endocrine disorder affecting individuals of reproductive age. This condition is characterized by a hormonal imbalance, which can lead to various symptoms and complications. Medically, PCOD is classified by the presence of multiple cysts in the ovaries, which can be observed through imaging tests such as ultrasounds.
One of the primary symptoms associated with PCOD is irregular menstrual cycles, which may manifest as missed periods or unusually heavy menstrual flow. Individuals may also experience excessive hair growth, known as hirsutism, which can occur in areas such as the face, chest, and back, resulting from elevated androgen levels. Acne and oily skin are additional symptoms that many may encounter, contributing to physical and emotional distress.
The etiology of PCOD is complex and multifactorial, with genetic predisposition playing a significant role in its onset. Family history of similar disorders can increase the risk of developing PCOD. Hormonal imbalances, particularly concerning insulin resistance and androgen levels, are crucial factors contributing to the symptoms experienced by those affected. Lifestyle influences, including obesity, lack of physical activity, and dietary habits, are also linked to the exacerbation of PCOD symptoms.
To diagnose PCOD, healthcare professionals typically conduct a comprehensive evaluation that includes a thorough physical examination to assess symptoms. Ultrasound imaging is utilized to visualize the ovaries and identify cysts, while blood tests help determine hormone levels, including testosterone and insulin. These diagnostic processes are vital to establishing an accurate diagnosis and formulating an effective management plan for those with PCOD.
Dietary Guidelines for Managing PCOD

Managing Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) effectively requires careful attention to dietary choices. A balanced diet rich in whole foods can significantly alleviate symptoms associated with this condition. Emphasizing nutrient-dense foods aids in managing insulin resistance, a common concern for individuals with PCOD. It is essential to focus on integrating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into daily meals to support overall health.
Including high-fiber foods, such as legumes, nuts, and seeds, helps regulate blood sugar levels and can be beneficial for improving insulin sensitivity. Healthy fats, particularly those found in avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish, should also be included in the diet, as they assist in hormone regulation and provide essential nutrients. Furthermore, lean protein sources like poultry, fish, and plant-based proteins are vital for maintaining muscle mass and promoting satiety.
To better manage PCOD symptoms, portion control and meal timing are crucial elements to consider. It is advisable to eat smaller, balanced meals throughout the day rather than large meals. This strategy aids in stabilizing blood sugar levels and helps in managing appetite. Additionally, mindful eating practices can enhance the overall eating experience, ensuring proper digestion and nutrient absorption.
Avoiding processed foods and added sugars is imperative, as these can contribute to weight gain and worsen insulin resistance. Instead, focus on whole, unprocessed options.
Furthermore, meal prepping can be an effective strategy to ensure access to healthy meals throughout the week, reducing the likelihood of impulsive eating choices.
Healthier snack options, such as fruit, yogurt, or mixed nuts, can also sustain energy levels while contributing to overall health.
Effective Exercises to Alleviate PCOD Symptoms
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) is a condition that can significantly impact a woman’s physical and emotional well-being. Incorporating regular physical activity into one’s lifestyle is crucial for managing PCOD symptoms effectively.
Exercise can aid in weight management, improving insulin sensitivity, and lowering stress hormone levels. This, in turn, can lead to a reduction in symptoms associated with PCOD.
Aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling, are particularly beneficial as they help burn calories and promote cardiovascular health. Engaging in aerobic activities for at least 150 minutes weekly can help in maintaining a healthy weight, which is often a challenge for those with PCOD. These exercises can also enhance insulin sensitivity, thereby improving overall metabolic function.
In addition to aerobic workouts, strength training should be incorporated into the routine at least two to three times a week. This type of exercise not only helps in building lean muscle mass but also contributes to increased resting metabolic rate. Exercises such as weightlifting, resistance band workouts, and bodyweight exercises (like squats and push-ups) can all be effective in enhancing muscle strength and promoting weight loss.
Flexibility workouts, including yoga and stretching exercises, play a vital role in managing stress, which is often elevated in women with PCOD. Yoga can provide several benefits, including relaxation and hormone regulation, which can be advantageous for those suffering from PCOD symptoms.
Setting realistic fitness goals is essential in a successful exercise regimen. Women should aim for gradual progress rather than immediate transformations. Establishing a workout schedule that fits into one’s daily routine can help maintain consistency. Moreover, incorporating small, achievable goals helps in creating a sense of accomplishment and encourages long-term adherence to an exercise routine.
Myths and Facts About PCOD: Debunking Misconceptions
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) is frequently surrounded by various myths and misconceptions that can lead to misunderstandings about the condition. One common myth is that PCOD is solely an infertility issue. While it is true that PCOD can affect fertility, it is a complex hormonal disorder with varying symptoms that impact multiple aspects of health, including metabolism and emotional well-being.
Another prevalent myth suggests that PCOD only affects overweight women. In reality, women of all body types can develop this condition. While weight gain can exacerbate the symptoms of PCOD, it is not a universal characteristic of all affected individuals. This misconception can lead to societal stigma, causing emotional distress for those struggling with the condition but who may not fit this stereotype.
Additionally, many believe that PCOD is entirely curable. Currently, there is no definitive cure for PCOD; however, various treatment options are available to manage symptoms. These treatments may include lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and regular exercise, as well as medical interventions like hormonal therapy. Education about this aspect can empower women to take control of their health and make informed choices regarding their bodies.
Women with PCOD often face emotional challenges due to the societal pressures and stigmas associated with this disorder. Recognizing that PCOD is a medical condition requiring understanding and support, is crucial in mitigating the emotional burden. Furthermore, it is essential for women to be well-informed about reproductive options available to them. Knowledge about fertility preservation and alternatives, such as IVF, offers hope and reassurance for those planning a family.
In essence, debunking these myths and presenting factual information about PCOD is vital for fostering understanding and support among affected individuals and their families. Awareness can assist in breaking down barriers and encouraging healthier conversations surrounding PCOD.